Blog
3D Printed Microfibers Could Provide Structure for Artificially Grown Body Parts
3D Printed Microfibers Could Provide Structures for Cell Growth
Science has come up with a new way to grow tissue and hence body parts using a simple off the shelf 3D printer. The 3D printer is used to make a structure or foundation over which cells can be grown. Much like a building needs a foundation or a car needs a frame, Researchers have used the same principal to grow cells over the 3D printed microfibers.
Problems with current methods of getting tissue or body parts:
Donors have to be got in order to get replacement tissue or any body part for that matter. Donors can be dead or alive to donate an organ. Many problems are associated with getting an organ from a donor. For one it may be expensive and also there is a question of getting your exact match. There are also donor lists to cross over before any organ can be received.
Making a complex structure of tissue such as bone to cartilage, right now uses a micro extrusion bio printer, which is very expensive.
All methods of getting or growing tissue these days are expensive and are not easily accessible to the common man. Plus these current methods grow the tissue separately and then combine them with an adhesive whereas in the body these tissues grow seamlessly together. Researchers now have found a novel, cheap and effective way to create organ tissue using 3D printed microfibers.
How does 3D printed Microfibers Work?
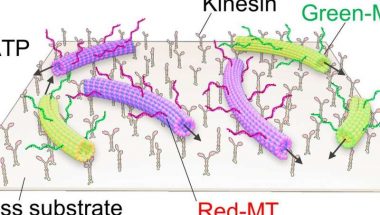
3D printed microfibers use a combination of 3D printing and elctrospinning. Electrospinning is a method that uses an electric charge to spin 3D printed microfibers from a polymer melt or some other solution into a desired pattern.
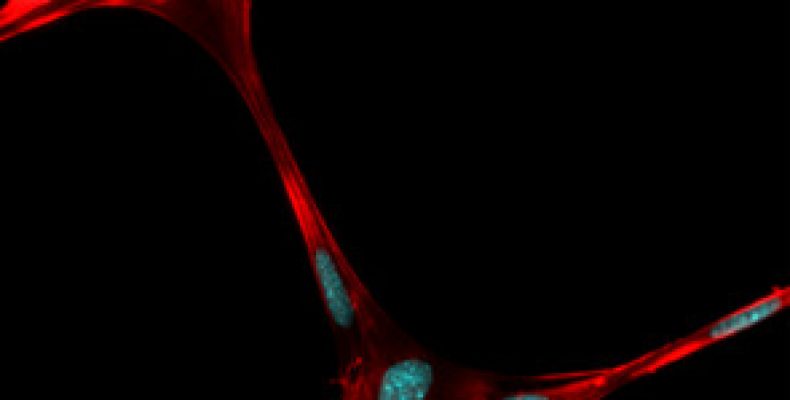
Once the pattern is made using the 3D printer, the 3D printed microfiber pattern is then deposited into hydrogel and then cells are grown onto the pattern.
Once the cells have fully grown onto the 3D microfiber pattern, the microfibers dissolve leaving only the cells in its place.
This novel method of 3D printed microfibers could have a lot of uses when it comes to the medical field.
Uses of 3D printed Microfibers:
3D printed microfibers could be used to create different tissue patterns and hence potentially grow different tissues requiring different tissue structures. This novel method of 3D printing microfibers could also be used to create complex tissue structures such as bone to cartilage together, instead of growing them separately and then using an adhesive or some other connector to join them.
How efficient will 3D printed microfibers be?
3D printing microfibers use an off the shelf 3D printer without making any major modifications. The electrospinner replaces the nozzle on the 3D printer and that is all the modifications that are necessary.
The 3D printer prints the exact pattern of the tissue and the pattern can be changed to print various other tissue types as well.
The 3D printed microfibers also dissolve when the cells have fully grown on the structure thereby leaving no foreign material residue in the organic material.
Right now experiments have been used to grow only less than 1 inch of tissue.
This cheap and effective method of growing tissue using 3D printed microfibers has far reaching possibilities when it comes to tissue growth.