Blog
What is IPv6 Address, Why Should I Know about It?
Everything you need to know about the IPv6 Address?
The world is not happening and exciting without the internet and a number of people will swear by it. When it comes to connecting with the internet not everyone know the silent technical world behind. In this Internet Protocol Version 6 ( IPv6) plays a vital role in allowing the communication and data transfers over the network.
It was developed way back in 1998 with an aim of replacing the earlier protocol named IPv4. For ages we made use of the IPv4 which consisted of four strings and each of this string had three digits separated by a simple dot. It was a 32 bit network protocol which had the ability to allow as many as 4.2 billion unique IP address.
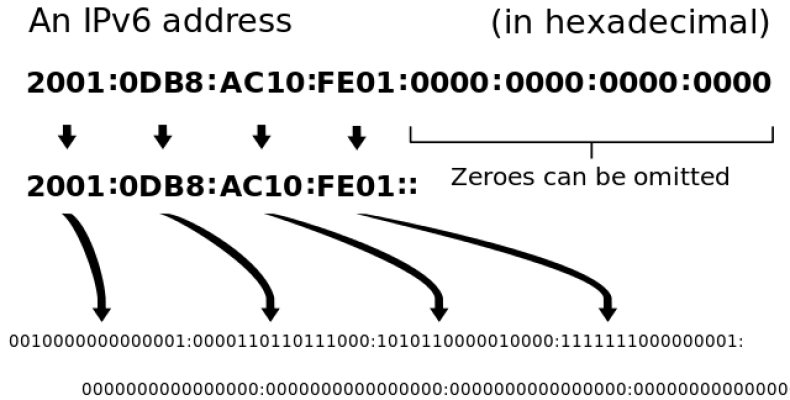
The different types of IPv6 address
A Unicast Address helps in identifying a unique node present on the network while multicast addresses simply represents a group of IP devices. Then comes ‘anycast addresess’ which is usually assigned to a set of interfaces which happens to belong to a number of different nodes.
How different is IPv6 from IPv4?
The major difference between the two the presence of a larger address space. The length offered by the IPv6 is 128 bits whereas the IPv4 offered just 32 bits. Secondly IPv6 is a beast when it comes to multicasting wherein a single packet can be sent to multiple destinations through a single send operation. Internet Protocol Version 6 comes with a new packet format which is specifically designed to lower the packet header processing for the routers.
It is worth noting that there is remarkable different between the headers of the IPv6 and IPv4 and another thing noticeable is that these protocols are not interoperable in nature. When it comes to transport and application-layer protocols there aren’t much difference when it works on the IPv6 but there might be some conflicts when running the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or Network Time Protocol (NTP). One of the best thing about IPV6 is that it helps in enhancing the privacy of the networks as it makes use of highly unique IP addresses which can help in identifying the devices on the global scale upon analyzing its network activity.
Some of the advantages offered by IPv6
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) offers a number of advantage over the earlier protocol by being highly reliable, secure, fast and efficient. Apart from simply offering more addresses it also brings a number of unique features which aren’t available on the IPv4. It makes it relatively easier and smarter to assign addresses and aids in network numbering and furthermore it helps in enhancing the routers efficiently connects with the different providers. Internet Protocol Version 6 ( IPv6 ) is great at standardizing thereby fixing the size of the host identifier portion of any given address in the 64 bits thereby helping to form a link layer. As stated earlier it also helps in boosting the security to a next level which can’t be experienced on the IPv4.
Shell scripting for network engineers helps them to learn shell scripting concepts networking and networking protocols and help them to use TCL (Tool Control Language) scripting effectively in most of the router platforms.