Blog
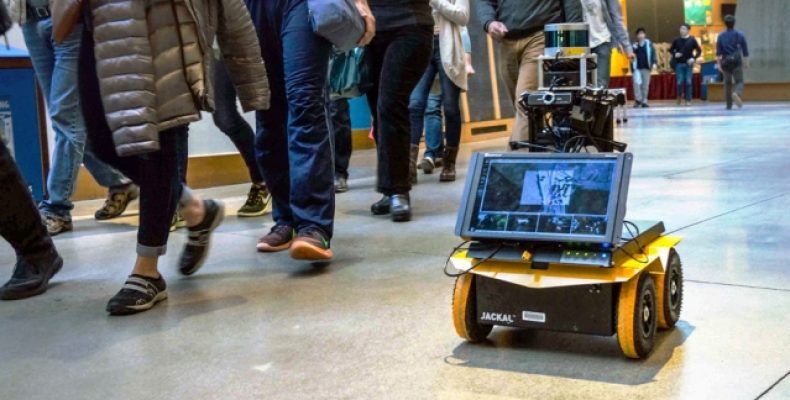

New Robot Rolls with the Rules of Pedestrian Conduct
Robot rolls with the rules of pedestrian conduct
In the same way that drivers follow the traffic code, most pedestrians follow certain social codes when it comes to moving through a crowded public thoroughfare: staying on the right, overtaking on the left, maintaining a respectable distance, and be prepared to deviate or change trajectory in order to avoid obstacles, while maintaining a steady pace of progress.
Now, engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, United States, have designed an autonomous robot with “socially conscious navigation” that can travel between pedestrians while respecting the general codes of conduct of the pedestrians The system of locomotive behavior used in this robot could allow other robots to move through hospitals, shopping malls and other areas with a lot of pedestrian traffic.
In tests carried out at MIT facilities, the robot was able to avoid collisions while maintaining adequate speed in its advance, in line with the average pedestrian flow.
The investigation is the work of Yu Fan team “Steven” Chen, Michael Everett, Miao Liu and Jonathan How.
For a robot to be able to move autonomously through an environment with a lot of pedestrian or vehicle traffic, it must solve four main challenges: location (knowing exactly where it is located), perception (recognizing its surroundings), movement planning optimum to a given destination) and control (physically perform the desired path).
For perception, Chen and his colleagues equipped the robot with sensors already available, such as webcams, a depth sensor and a high resolution LIDAR sensor. For localization, they used open-source algorithms in order to map the robot environment and determine its position. To control it, they used models already used for autonomous land vehicles.